Introduction
Almost all clients start off with a clean SAP Security and Role design. But as time passes, SAP upgrades, changes in business processes, AMS contract changes, custom transactions, etc. all these factors slowly degrade the quality of the security. And before the client knows, it becomes really difficult to make sense of the security and roles. One of the challenges that is faced by the security administrator is figuring out which authorizations are linked to which transactions. Two fundamental components in SAP security are SU24 and USOBT_C, which help to deal with this challenge. In this blog post, we’ll delve into what these components are and why they are crucial for a cleaner SAP security environment.
SU22 Default Data Maintenance (SAP)
SU22 transaction in SAP can be used to view the SAP standard authorization default values for SAP applications (read – Transactions, FIORI services, Web Dynpro etc.). Default authorization values for standard SAP applications are delivered via an upgrade, support package deployment, or SAP Notes. This SAP-provided data is displayed and maintained in transaction SU22. The values in SU22 come from the tables USOBT and USOBX.
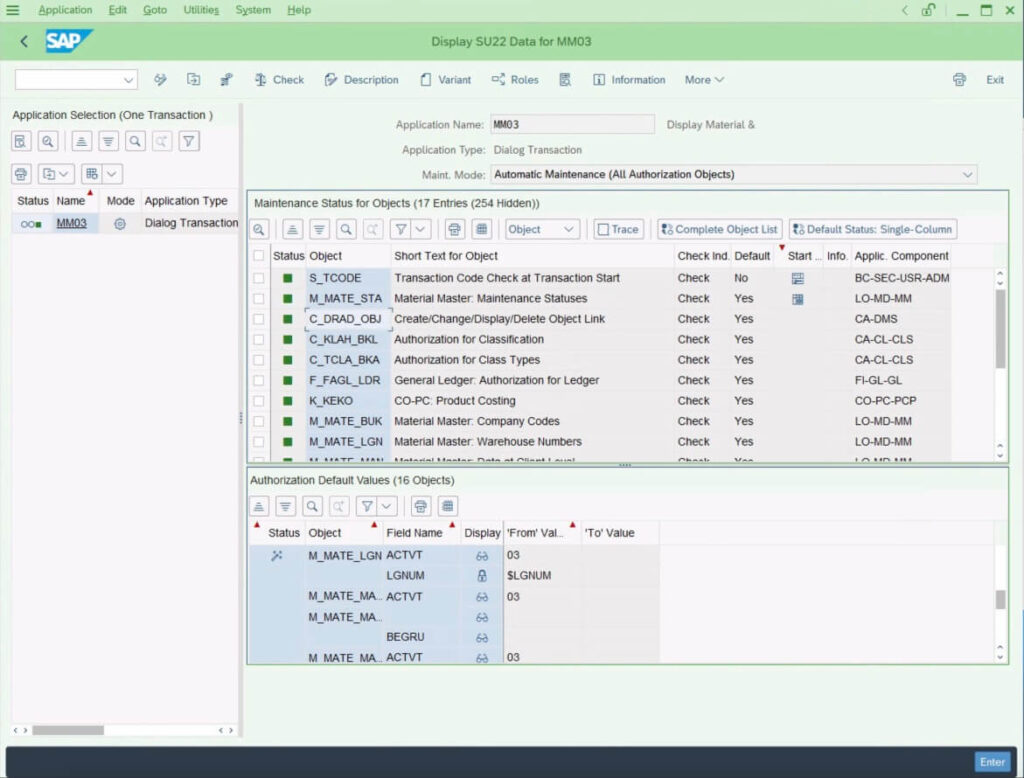
The important thing to remember is you should never change values in SU22 transactions, for updating any values a different transaction SU24 must be used. You can think of this as How we should never update SAP-provided PFCG Roles, instead, we should copy them to a customer version Z* and then update them. Now let’s look at SU24.
SU24 Authorization Default Data (Cust.)
SU24 transaction in SAP is “Maintain Authorization Default for customer” Values. SU24 provides a comprehensive view of the authorization objects relevant to specific transactions, including fields and values that are checked during runtime. The values in SU24 come from the tables USOBT_C and USOBX_C. If you notice the table names are like SU22, with an additional “_C” suffix, this stands for Customer.
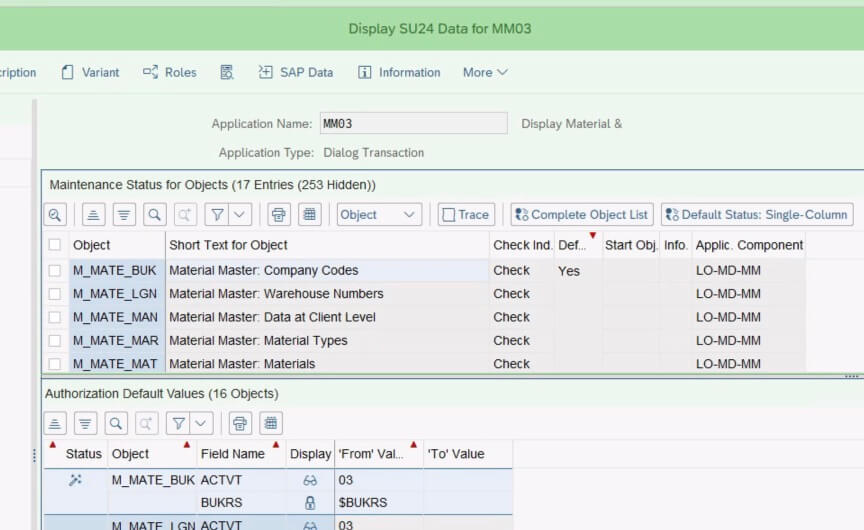
SU24 is where a system administrator can change the authorization defaults as per the customer. In SU24 admins must only map the authorization object which is really needed by the transaction. Also, the values for these object fields must not be maintained as “*”, unless the transaction really needs it.
Bonus: SU25 transaction is used to (initially) transfer the USOBT values to the USOBT_C table. But this is a topic for another blog.
PFCG – Profile generator
The profile generator (PFCG transaction) gets its data from these _C tables, or SU24 transaction. When you add a new transaction to the PFCG Role Menu and maintain the Authorizations. Authorization object values from SU24 with “Check Indicator” status set as “Check” is pulled added into the role profile.
The authorization objects will have values as standard, partially maintained or not maintained at all. Regardless of the authorization values fetched by the PFCG from SU24, a system administrator should always review and maintain the values as per the customer’s requirements.

Mapping the correct values in SU24 really helps administrators when creating and maintaining the PFCG roles.