In SAP, common security transactions are used to manage user authorizations, roles, profiles, and other security-related configurations. Below are some of the commonly used security transactions along with their descriptions:
SU01 – To create and maintain the users.
SU01D – To Display Users.
SU10 – For mass maintenance.
SU02 – For Manual creation of profiles.
SU03 – For Manual creation of authorization.
SU3 – For setting Address and default parameters.
PFCG – For maintaining role using profile generator.
PFUD – For Comparing User master in Dialog.
SUPC – For generation of Mass profile.
SU24 – For Maintaining Authorization Check Indicators and for Maintaining templates.
SU25 – For initial Customer table fill (SU24).
SU20 – Lists down the authorization fields.
SU21 – Lists the Object classes and authorization objects.
SM01 – For locking the transaction from execution.
SM19 – Security audit – configuration.
SM20 – Security audit – reporting.
SM30 – For creation of table authorization groups and for maintaining assignments to tables
STMS – Transport Management System
RZ10 – Profile configuration
RZ11 – Maintain profile parameters
SU53 – To display last authority check that failed
SU56 – Display User buffer
SECR – Audit Information System
ST01 – System Trace
STAUTHTRACE – System Trace for Authorization checks(Better than ST01)
SUGR – Maintain User groups
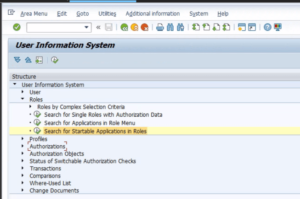
SUIM – User Information System
SU05 – Maintain Internet Users
SMLG – Maintain Logon Group
ST02 – Setups/Tune Buffers
SM02 – System Messages
SM04 – User Overview
SM12 – Display and Delete Locks
SM13 – Display Update Records
SM21 – System Log
SM50 – Work Process Overview
SM51 – List of SAP Servers
SM59 – Display/Maintain RFC Destinations
ST11 – Display Developer Traces and error log files
ST22 – ABAP/4 Runtime Error Analysis
SM35 – Batch Input Monitoring
ST05 – Performance trace
These transactions are critical for managing SAP security and ensuring that users have the appropriate authorizations to perform their job functions. It’s important to use them responsibly and follow best practices for SAP security. Additionally, regular monitoring and auditing of user authorizations are essential to maintain a secure SAP environment.